Many people don’t realize it, but there is a strong connection between physical exercise and effective diabetes management, especially when it comes to type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance (don’t know what insulin resistance is? Check out our previous post). Physical activity is far from being just a supporting habit in diabetes care; it is a core component of a treatment plan, capable of regulating and improving glucose metabolism, increasing insulin sensitivity, strengthening the cardiovascular system, and promoting both physical and mental well-being for those living with this chronic condition.
Understanding Insulin Resistance
To better understand how physical exercise impacts diabetes, we need to dive a little into physiology and the metabolic imbalances that characterize insulin resistance. Insulin, secreted by pancreatic beta cells in response to rising blood sugar levels after meals, helps with the uptake, use, and storage of glucose in tissues—mainly skeletal muscle and fat tissue. This action is essential to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range, preventing both hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia.
When we talk about insulin resistance, we’re referring to a complex state often linked to obesity, sedentary lifestyle, genetic predisposition, and other risk factors, where insulin can no longer act properly. This leads to a reduced ability of cells to absorb glucose, resulting in blood sugar buildup (hyperglycemia). Over time, this can contribute to the onset of type 2 diabetes. It’s not just about sweets—calorie-dense foods of all kinds can contribute to this condition.
Physical Exercise

Regular physical activity can be life-changing for individuals with diabetes, improving glycemic control and overall health. When we exercise, especially during resistance training, our muscles contract in ways that allow glucose to enter cells without the need for insulin. This effect helps reduce blood sugar levels—even for those with insulin resistance.
Improving Insulin Sensitivity

Exercise increases insulin sensitivity over time. This means that insulin becomes more effective at transporting glucose into cells, which helps manage blood sugar levels during rest and after meals.
Supporting Beta Cell Function
For those with type 2 diabetes, progressive loss of pancreatic beta cell function is a challenge. Exercise may have a protective effect on these cells, potentially improving their ability to secrete insulin.
Fat Metabolism and Inflammation
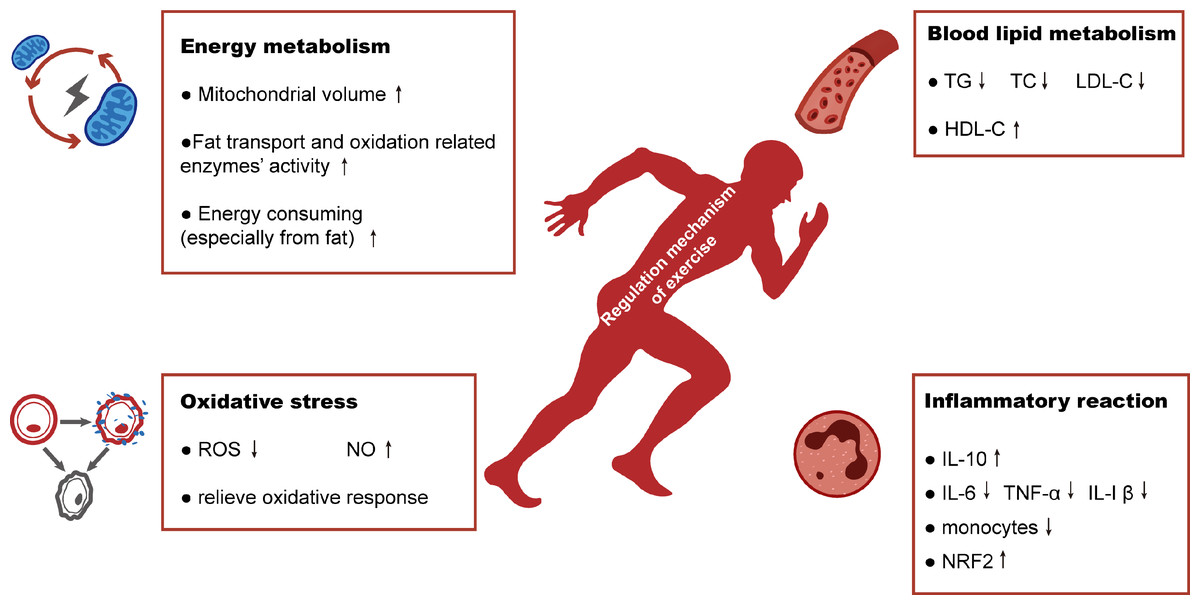
Exercise helps balance fat levels in the blood, reduces harmful triglycerides, increases HDL (good cholesterol), and lowers LDL (bad cholesterol). It also reduces chronic inflammation, which contributes to insulin resistance and diabetes complications.
Cardiovascular Benefits
People with diabetes are at higher risk for cardiovascular disease. Regular exercise improves cardiovascular function, lowers blood pressure, improves blood vessel health, and reduces the risk of blood clots.
Exercise Prescription
Exercise for individuals with diabetes must be personalized. It’s essential to consider the type of diabetes, glycemic control level, comorbidities, physical capacity, and personal preferences to ensure safety and adherence.
Type 1 Diabetes and Physical Activity
Although type 1 diabetes is primarily managed with insulin, physical activity supports general health. However, adjustments in insulin dosage and carbohydrate intake are necessary to avoid exercise-induced blood sugar imbalances.
Is Exercise Indispensable in Managing Diabetes?

Physical activity is more than just a lifestyle recommendation—it’s a core therapy for diabetes management. With its broad benefits—from improved glucose control to reduced inflammation and cardiovascular risk—exercise is essential in preventing and managing type 2 diabetes and insulin resistance.
🎥 Watch: How Physical Exercise Helps Control Diabetes
To complement what you’ve just read, check out this informative video that clearly explains how physical activity supports diabetes management:
Source: https://youtube.com
Check more here: https://www.vivviral.com/category/living-with-diabetes/



